Key Components of an RFID System and How They Work

22/11/2023
Depending on the purpose and specific application needs, each RFID system can be configured differently. However, any RFID system will typically consist of the following core components:
- RFID Reader
- RFID Antenna
- RFID Tags
- Data Processing System
- User Interface
- Cabling
The simplest RFID system may include a handheld or mobile reader (with a built-in antenna) and RFID tags. In contrast, more complex systems are designed using multi-port readers, additional functional devices (such as indicator lights or buzzers), multiple antennas and cables, and dedicated management software.
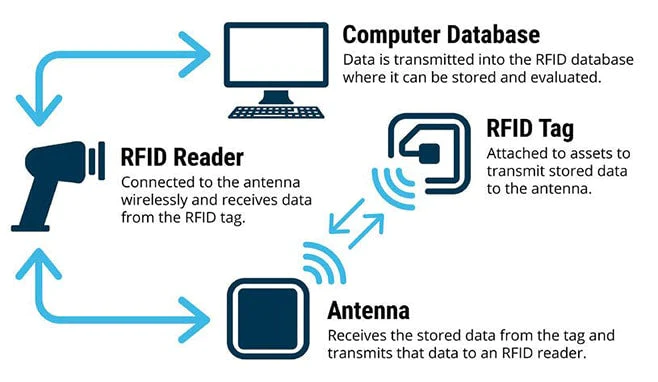
RFID Reader
The RFID reader is considered the “brain” of any RFID system and is essential for its operation. It is the device that transmits and receives radio frequency signals to communicate with RFID tags. RFID readers are typically divided into two main types: fixed readers and mobile readers.
Cost of RFID Readers
The reader is usually the most expensive component in an RFID system. Prices typically range from VND 8 million to 70 million (approximately USD 300–2,800), depending on the type and features.
Fixed RFID Readers
These are installed in a stationary position, often mounted on walls, desks, entry gates, or other designated locations. Fixed readers are usually connected to external antennas for enhanced performance. This setup ensures a clean, aesthetic look and is suitable for scanning RFID tags indoors where product volume is moderate.
Mobile RFID Readers
These are handheld devices that allow flexible tag reading while still transmitting data to a server or other systems. Mobile readers come in various form factors depending on the use case or environment—for example, designs that resemble a wristwatch, smartphone, or tablet.



RFID Antenna
The RFID antenna is an essential component of any RFID system. Its primary role is to convert the signal from the RFID reader into RF (radio frequency) waves that RFID tags can receive. Without an RFID antenna, the reader would not be able to accurately transmit and receive signals from tags. Antennas can either be built into the reader or installed separately as external units.
Unlike RFID readers, RFID antennas are passive devices, they receive power directly from the reader. When energy is transmitted from the reader to the antenna, the antenna generates an RF field, which is then broadcast to tags within the area. The antenna’s ability to focus energy in a specific direction is called its gain. Simply put, the higher the gain, the stronger and farther the RF field extends.
Types of RFID Antennas: RFID antennas, like most RFID components, come in various types based on several criteria:
- Frequency ranges: 902–928 MHz, 865–868 MHz, 860–960 MHz
- Polarization: Circular or linear
- Deployment environment: Indoor or outdoor use
- Read range: Short-range or long-range
- Form factors: Shelf antennas, floor antennas, panel antennas, gate antennas
Investment cost: Most RFID antennas range from VND 1 million to 10 million (approximately USD 40 to 400). However, certain specialized antennas may cost more depending on their capabilities and industrial requirements.
RFID Tags
At their simplest, RFID tags consist of two parts:
- an antenna that transmits and receives signals, and
- an RFID chip (or integrated circuit, IC) that stores the tag’s unique ID and other data.
RFID tags are attached to assets, goods, or animals to track them using RFID readers and antennas. The tag transmits data about an object—such as inventory items, assets, or animals—via radio waves to an antenna-reader system.
The most common RFID tags are passive, meaning they do not contain a battery (unlike active tags). They receive energy from radio signals emitted by the reader. Once a tag picks up a signal from the reader/antenna, that energy powers the chip, which modulates the response with stored data and sends it back to the antenna/reader.
Data Processing System
The data processing system receives information from the RFID reader and processes it to fulfill specific application needs. This system may include: computers, management software, databases, analytics tools.
It transforms raw RFID data into actionable insights and automates decision-making processes.
User Interface
The user interface provides a way to interact with the RFID system, including displaying information, configuring devices, and monitoring operations. This interface may include components such as screens, keyboards, printers, or computer-based dashboards.
These components work together to form an efficient RFID system, enabling the automatic and accurate identification and tracking of objects.
How an RFID System Works
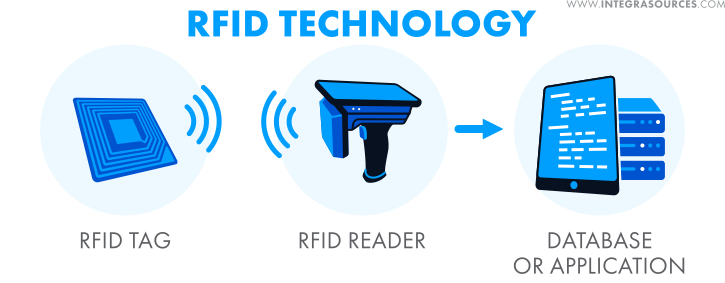
The operating principle of RFID technology is based on the interaction between three main components: the scanning antenna, the transceiver (reader), and the transponder (tag).
When the RFID reader and scanning antenna are combined, they form a system capable of reading RFID signals. The reader can be either a fixed device mounted in a stationary location or a mobile unit that can be carried around. It uses radio frequency waves to send an activation signal to the RFID tag.
When the RFID tag receives this activation signal, it responds by sending a return signal back to the reader via the scanning antenna. Through this exchange, the data stored in the RFID tag is transmitted to the reader.
The transponder, embedded in the RFID tag, is responsible for sending this return signal. The read range of each RFID tag can vary depending on multiple factors, including:
- The type of tag (passive, semi-passive, or active)
- The type of reader
- The RFID frequency used
- Environmental interference such as metal or liquids
Tags with stronger power sources (such as active tags) typically offer longer read ranges.
This process allows RFID systems to automatically identify and collect data from tags attached to items such as products, goods, animals, or people.
Related Articles
- 1Gate’s RFID-Based Traceability & Anti-Counterfeiting System
- Hệ thống truy xuất nguồn gốc và chống giả 1Gate
- RFID Applications in Steel Manufacturing Plants
- Choosing RFID Tags for Metal Surfaces – What You Need to Know
- UNIQLO Implements RFID on a Global Scale
- Walmart, RFID, and the New Retail Strategy
- Ứng dụng RFID trong nhà máy sắt thép
- Lựa chọn thẻ RFID gắn trên kim loại- Những điều cần lưu ý
- UNIQLO áp dụng RFID trên phạm vi toàn cầu





